Performance of Pediatric Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Organ Dysfunction Criteria in Late-Onset Sepsis in a Quaternary Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Case-Control Study - The Journal of Pediatrics

In ER, Electronic Alert Helps Detect Severe Sepsis in Children | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia

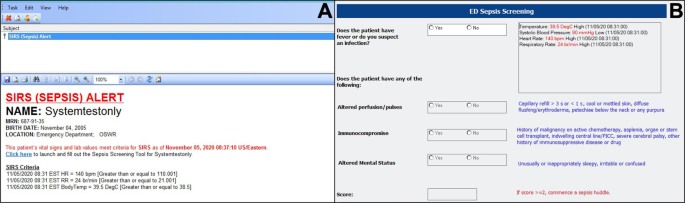
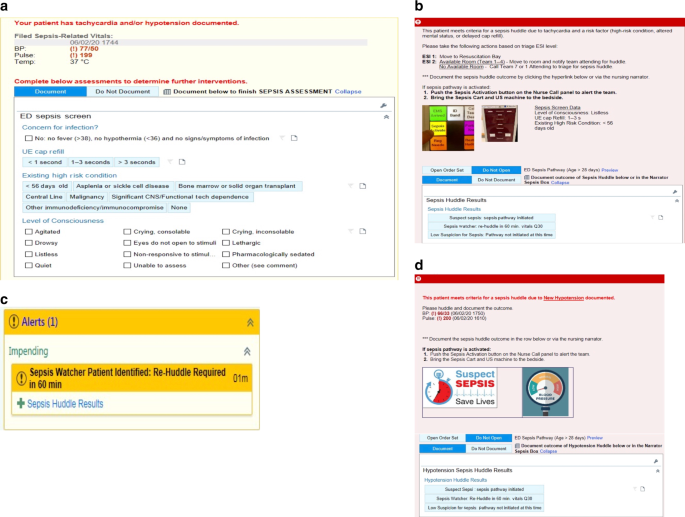
Improving Recognition of Pediatric Severe Sepsis in the Emergency Department: Contributions of a Vital Sign-Based Electronic Alert and Bedside Clinician Identification. - Abstract - Europe PMC
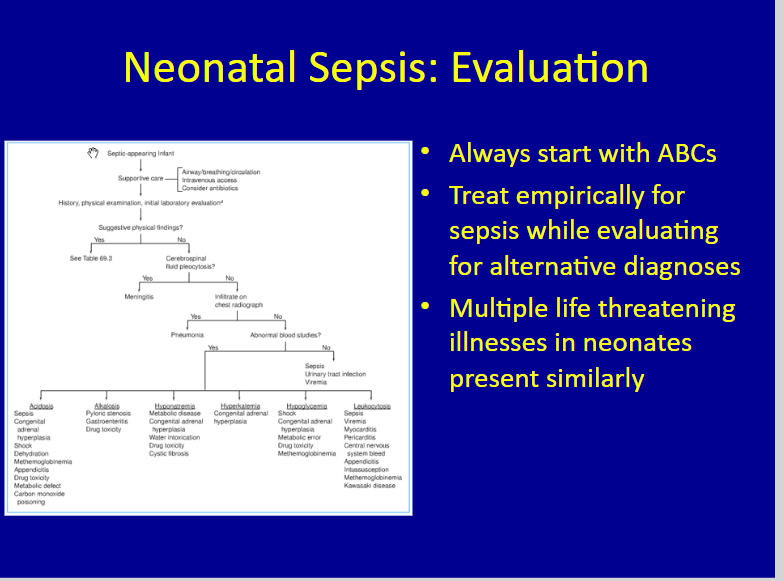
Emergencies In The First Month Of Life" - Intro And Case 1: Sepsis - Part 1 Of 4 - Lecture And Slides From CHOP With A Link To Newborn Fever Clinical Pathway - Tom Wade MD
Evaluation Of The Well Appearing Febrile Infant From CHOP – Part 4 Of 4 – 2 to 24 Months – Occult Bacteremia - Tom Wade MD
Improving Recognition of Pediatric Severe Sepsis in the Emergency Department: Contributions of a Vita
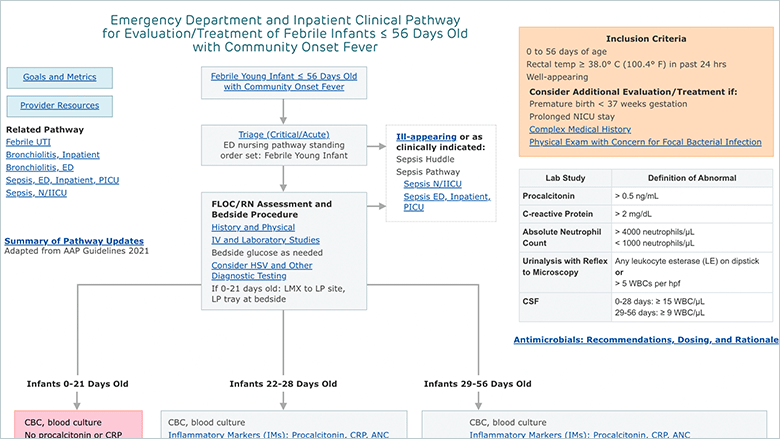
Febrile Infant Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department and Inpatient | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Machine learning models for early sepsis recognition in the neonatal intensive care unit using readily available electronic health record data | PLOS ONE
Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in

Emergencies In The First Month Of Life" - Intro And Case 1: Sepsis - Part 1 Of 4 - Lecture And Slides From CHOP With A Link To Newborn Fever Clinical Pathway - Tom Wade MD

PDF) Machine learning models for early sepsis recognition in the neonatal intensive care unit using readily available electronic health record data
Machine learning models for early sepsis recognition in the neonatal intensive care unit using readily available electronic health record data | PLOS ONE

Sepsis-Related Brain MRI Abnormalities Are Associated With Mortality and Poor Neurological Outcome in Pediatric Sepsis - Pediatric Neurology

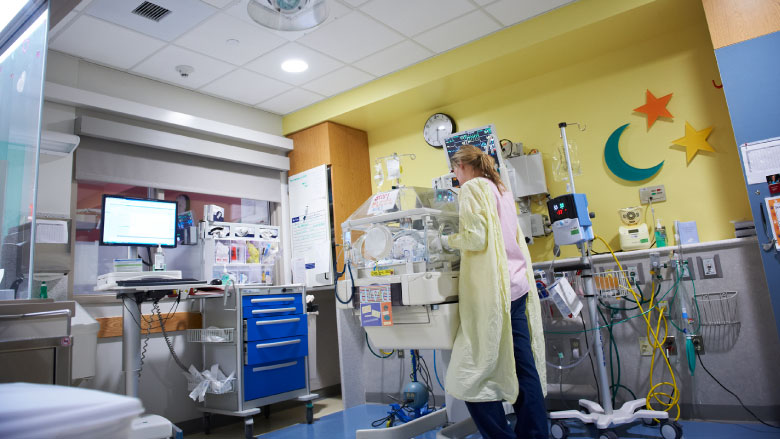
Researchers Use Data Tools to Rapidly Detect Sepsis in Sick Newborns | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia

Sepsis-Related Brain MRI Abnormalities Are Associated With Mortality and Poor Neurological Outcome in Pediatric Sepsis - Pediatric Neurology