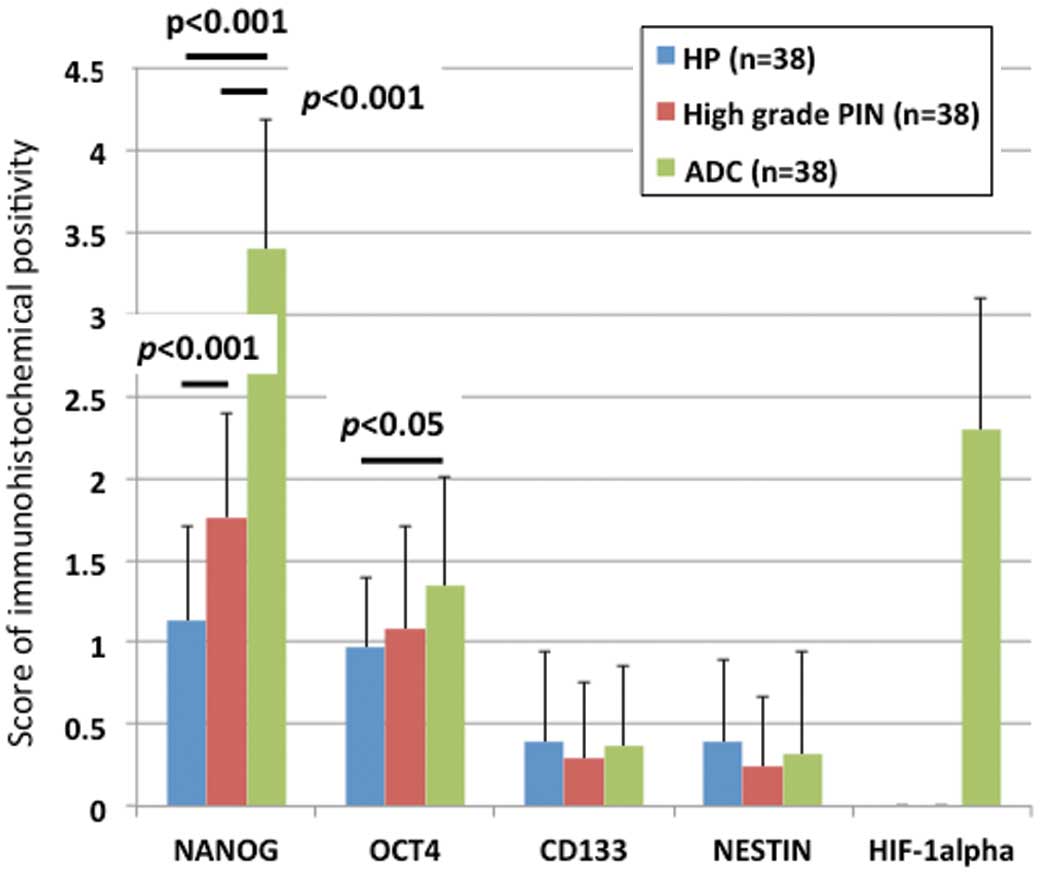
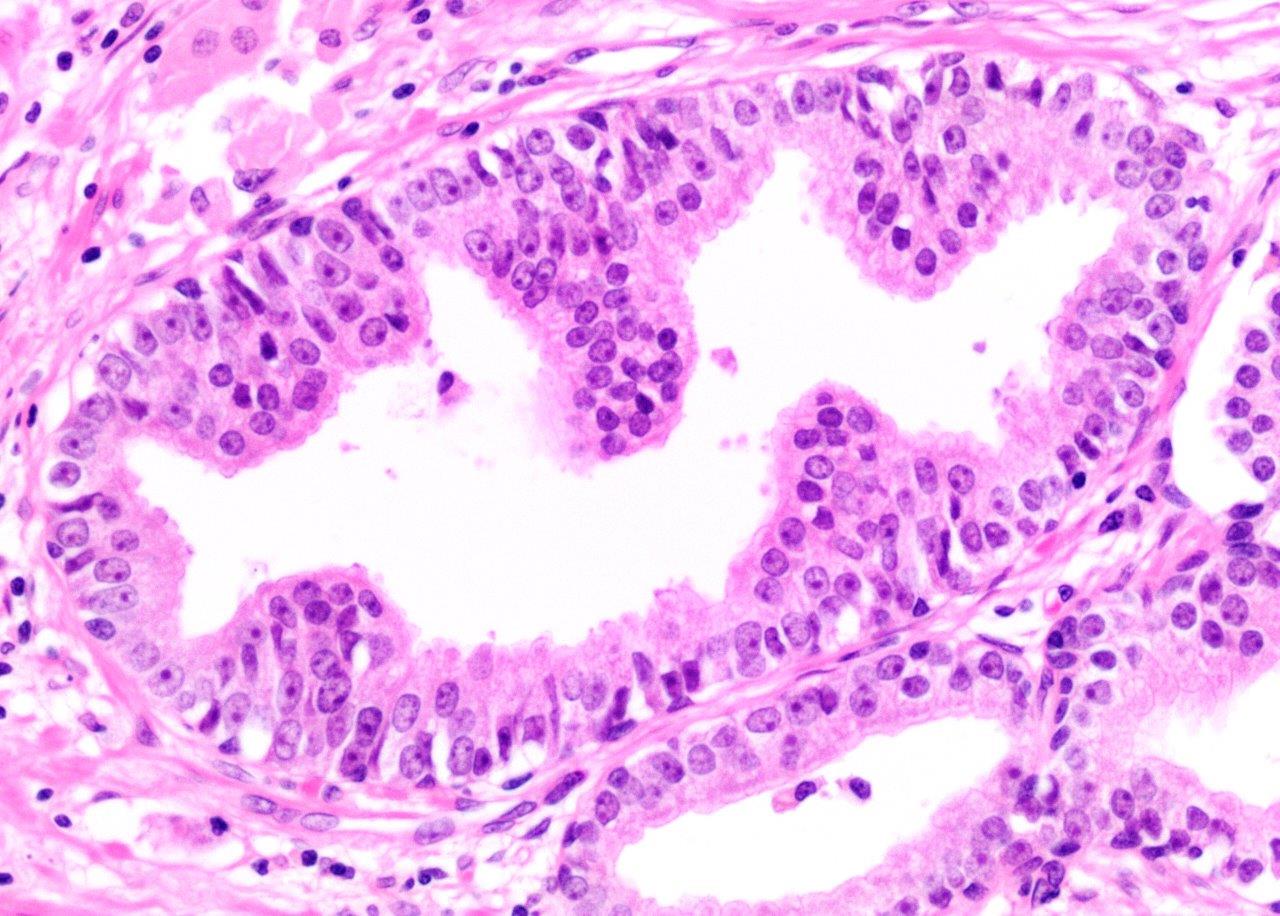
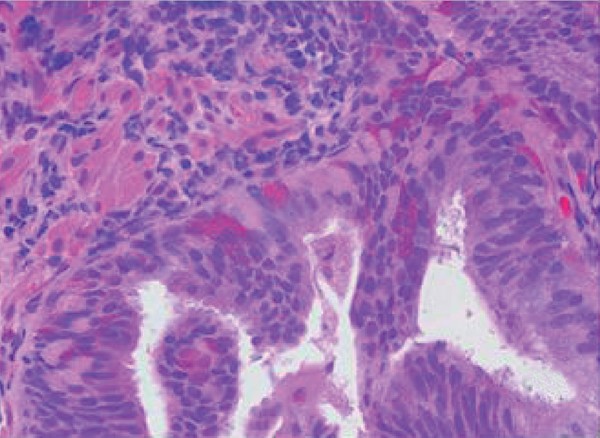
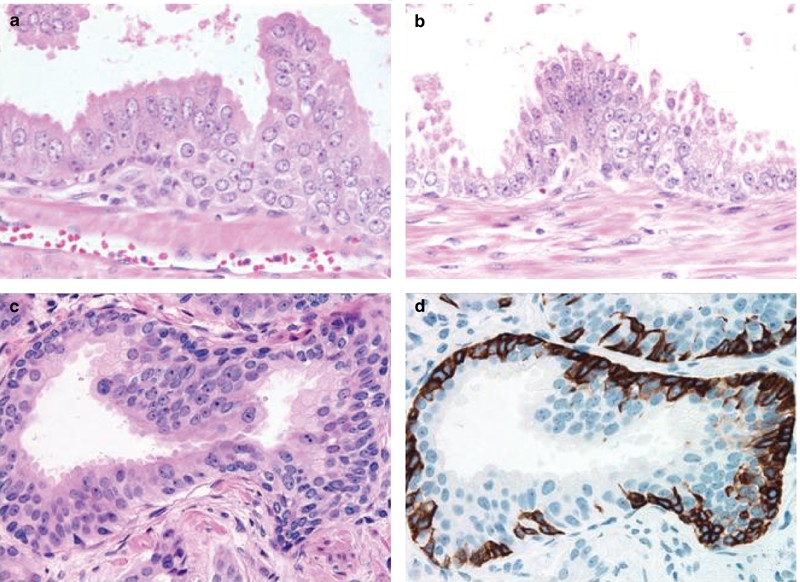
A: Photomicrograph of Benign prostatic leison (10x), B: Photomicrograph of Chronic Prostatitis (10x). C: figure of Basal cell hyperplasia (10x), D: Photomicrograph of Low grade PIN (40x). E: Figure of High grade

Morphological identification of the patterns of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and their importance | Journal of Clinical Pathology
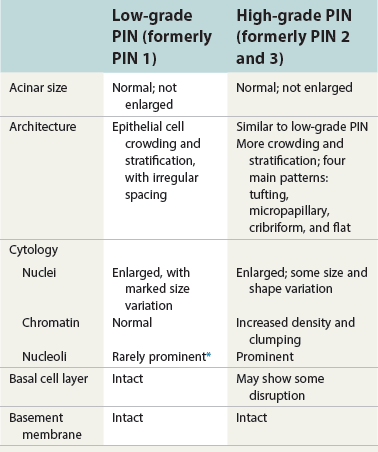
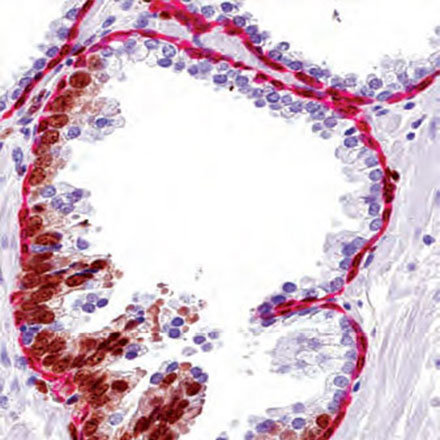
Preneoplastic Lesions in the Prostate: Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate | Basicmedical Key
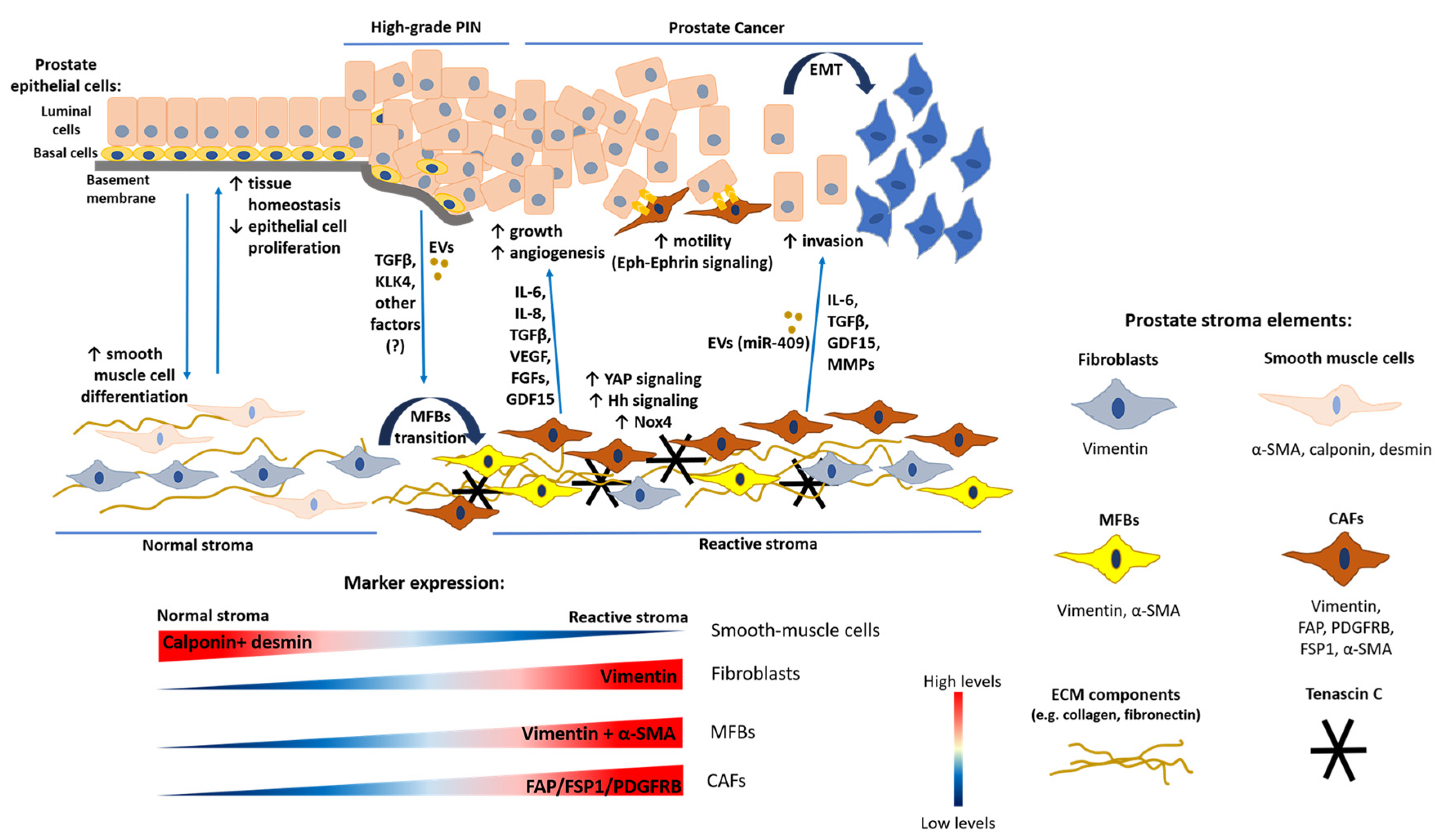
Cancers | Free Full-Text | The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Prostate Cancer Tumorigenesis
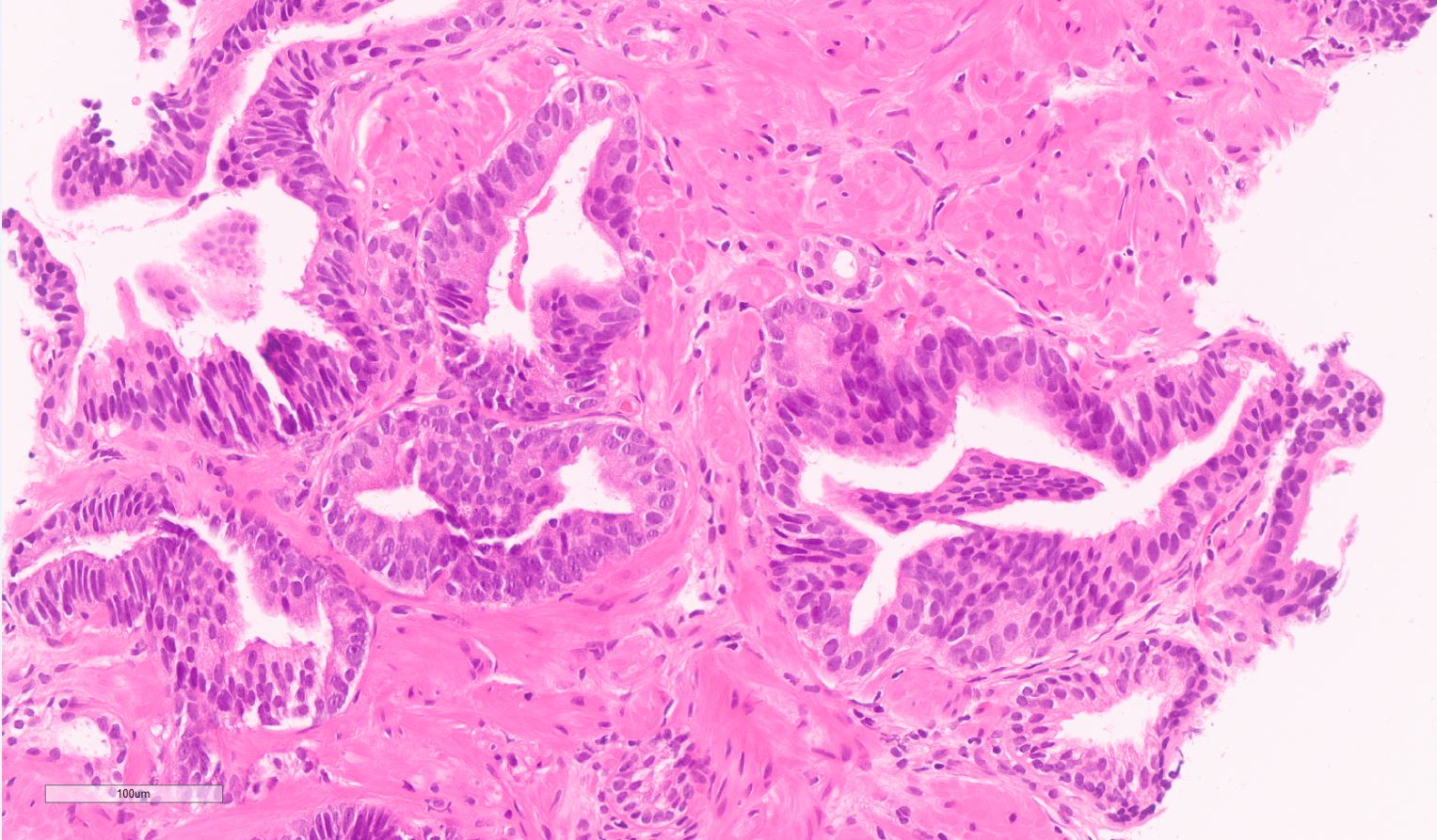
High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, PIN-like carcinoma, ductal carcinoma, and intraductal carcinoma of the prostate | Modern Pathology
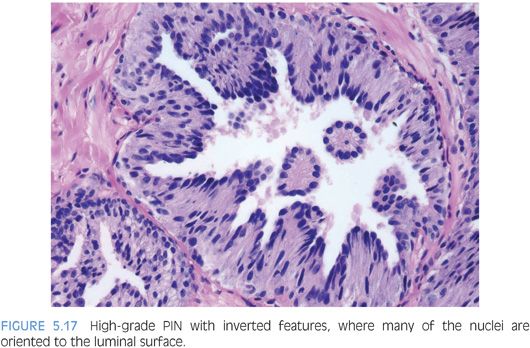
Preneoplastic Lesions in the Prostate: Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate | Basicmedical Key